RESEARCH 》 CDN Introduction - Content Delivery Networks or Content Distribution Networks
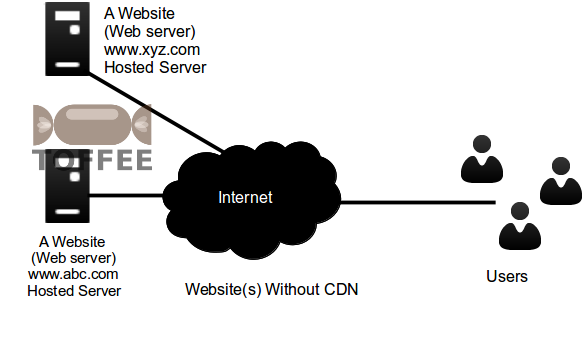
A Website without CDN Network: As everyone knows in a most common typical simplest scenario, you will have a website hosted in a web-server. In most
common cases a typical small website will be hosted in some web-server, provided by web-hosting service provider. And the website DNS domain name points to this
hosting web-server. In a simple scenario like this when the user requests the pages (or in general we can say any content such as text pages, images, and other
media), the end-user’s browser request reaches this web-server, and the web-server delivers the web-pages via HTTP Protocol.
Local user Browser Cache: The process of page or content download is pretty straight forward in a web-browser. A web-browser will have a small local cache. So that if there is any future repetitive requests, instead each time fetching from the main website (web-server), the browser will load/render the pre-cached content directly in the browser interface if it finds that specific content already once stored earlier in its cache. This saves up a lot of traffic. Since most of the times any website will have a lot of common content, such as logos, some Java scripts, CSS Stylesheets and so on. But the only drawback is that if there is a small organization, then each user have to access the content atleast once, so that they get their browser cache stored with content. In this case it is a highly discrete or non-shared cache platform/scenario.
Local web Proxy/Caching Servers: So in a office, or any such setup, where there are N users accessing common Internet resource, we can deploy a common web proxy or caching server(s). These servers (or a server) will create a great opportunity of creating a localized common caching scenario. So in this mode assume if one user accesses a website for first time, assume few of its contents are cached in this caching server, then later that day whichever other user accesses the same content, they may receive cached content from this central caching/proxy server. This is a huge advantage. Once the cache is mature and holds enough cached contents, it will sometimes exponentially reduce the network load, and downloading repetitive data from Internet (or any network in general).
A Website via CDN Network: In this scenario, the main basic website acts much like a source or origin. It will contain the web-content but it will not
serve the real end-users. Instead there is going to be a CDN Service provider, and his vast infrastructure with several distributed, so called CDN Nodes across
Internet spread globally. When the end-user requests the website, it is these CDN caching nodes will actually server the content to the end users. The job of the
CDN service provider is to provide a highly redundant load-sharing along with transparent/abstract infrastructure. The CDN provider will often point or assign a
CDN node which is least used at that instance, also sometimes assigns dynamically a CDN Node which is geographically nearer to the end-user. Hence this reduces
the download time, since it reduces the number of router hops in internet.
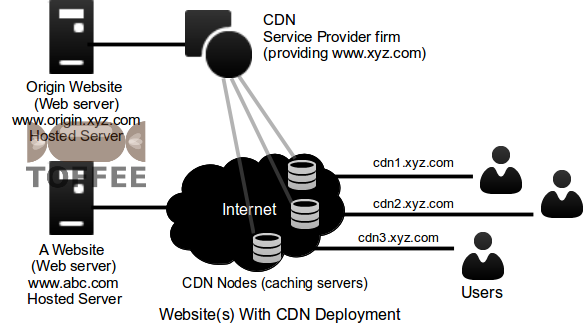
A CDN Node is often a highly proprietary caching resource installed by the CDN Service provider, where when it gets a request of a content to be served from end-user browsers, it caches the pages/content from its neighboring CDN Nodes, or sometimes directly from the origin web-servers. So this will exponentially reduces the load on the origin webserver. It is like with CDN server, the load on the origin webserver is or can be reduced upto 70-80% or sometimes even more depending on the content nature and depending on static vs. dynamic content it has.
So this is how a basic CDN works, its significance and value addition for any website if it is served to users via CDN, versus served directly via single webserver (or just few redundant web-servers) without a CDN.
Apart from this there are various advantages in using a CDN within your deployments. To know more about CDN Advantages kindly read the full detailed article HERE.
Suggested Topics:
Generic CDN
Building my own CDN
| 💎 TOFFEE-MOCHA new bootable ISO: | Download |
| 💎 TOFFEE Data-Center Big picture and Overview: | Download PDF |

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Featured Educational Video:

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
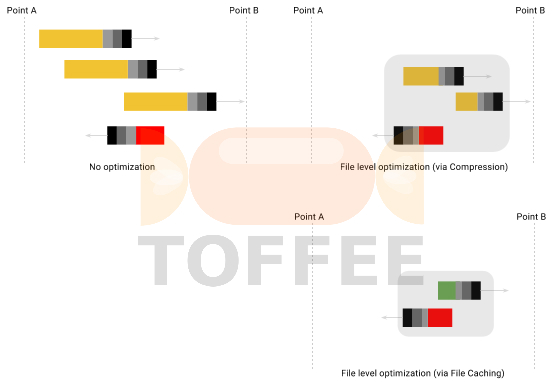
Research :: Optimization of network data (WAN Optimization) at various levels:
Learn Linux Systems Software and Kernel Programming:

Hardware Compression and Decompression Accelerator Cards:
![TOFFEE Architecture with Compression and Decompression Accelerator Card [CDN] TOFFEE Architecture with Compression and Decompression Accelerator Card [CDN]](http://sareesaremypassion.org/cdn/the-toffee-project/i/DOCUMENTATION/33/TOFFEE%20compression%20hardware.png)
TOFFEE-DataCenter on a Dell Server - Intel Xeon E5645 CPU:









