Documentation :: Documentation :: Guia de seleção de hardware TOFFEE
Written by: Kiran Kankipati - Published: 14-Dec-2016
Língua :: Inglês
Quando você cria um dispositivo WAN Optimization com TOFFEE, o processamento completo de pacotes (otimização de dados) ocorre
na camada de software ou, em outras palavras, mais precisamente, o espaço no kernel do sistema operacional. No entanto, se você tiver algum hardware de compactação ou criptografia
placa de hardware do acelerador, as partes dos módulos de processamento de pacotes TOFFEE podem ser descarregadas para a camada de hardware e, assim, melhorar sua
eficiência.
Mas o foco e o pressuposto neste guia são que você está usando uma plataforma de computação genérica como o PC / servidor / dispositivo IoT para construir um
Dispositivo de Otimização de WAN com a plataforma TOFFEE, uma vez que a opção de descarregamento de hardware só é viável para OEM grandes e outros comerciais
fabricantes de equipamentos. Portanto, é importante que, com base em suas velocidades de WAN dentro dos quais esses dispositivos TOFFEE sejam implantados, você precisa
Escolha as especificações de hardware conforme sugerido neste guia.
Compreendendo os benchmarks da CPU:
Apresentando TrueBench - um sistema de benchmarking de CPU de alta resolução:

TrueBench é um sistema de benchmarking exclusivo no qual o desempenho do sistema central e os parâmetros de eficiência são medidos em alta resolução extrema na ordem de vários
milhões/bilhões de segundos para uma determinada tarefa específica. TrueBench faz parte da pesquisa do projeto TOFFEE. Para mais detalhes: visite TrueBench
Aplicativos (casos de uso) do TrueBench:
- criando dispositivos de rede de alto desempenho de baixa latência
- avaliação do CPU (plataforma) embutida / SoC
- avaliação de hardware de servidor e datacenter
- Avaliação de design/arquitetura de produto novo
- Aplicações científicas (como HPC, Super-Computadores, etc.)
Escolhendo a CPU para o seu dispositivo TOFFEE:
Aqui está um guia definitivo que o ajudará a escolher a CPU para o seu dispositivo TOFFEE WAN Optimization. O código fonte TOFFEE é altamente modular.
Pode escalar ou reduzir o seu nível de otimização com base em seu hardware e, mais precisamente, o potencial de processamento da CPU. Dito isto, vamos assumir você
habilitaram todos os níveis de otimização. Nesse contexto, aqui está a tabela que dá uma idéia para escolher sua CPU de acordo com suas velocidades de rede WAN específicas de implantação:
NOTA: Esta tabela é derivada após ensaios, testes e pesquisas extensivos ao longo de vários anos. E também uma co-relação entre CPU benchmarks de desempenho de benchmarks (como TrueBench) versus benchmarks de multi-thread padrão versus desempenho em tempo real de TOFFEE durante processamento extensivo de pacotes de alta carga.
| CPU / Hardware | Specs | TrueBench Score | Velocidades WAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi3 Model B | 1.2GHz 64-bit quad-core ARMv8; 1GB RAM | 1,310,619,137 | <= 5-10Mbps |
| ARM Cortex-A53(ARMv8 64bit) (ODROID-C2) | 1.50 GHz, Quad Core, ODROID-C2 - IoT single board computer(SBC) | 949,003,080 | <= 10-20Mbps |
| Intel Atom D525 | 1.80 GHz, Dual Core, 13 W TDP | 874,076,069 | <= 20-30Mbps |
| Servidor high-end: Intel Xeon E3-1240 v3 |
91,632,198 | <= 300-600Mbps | |
| Desktop de ponta: Intel core i7 6700K |
44,200,382 | <= 700-900Mbps (1Gbps approx) |
Então, se você estiver construindo seu próprio dispositivo de Otimização de WAN (ou, em geral, qualquer dispositivo de rede), você pode comparar com TrueBench (como sugerido no site TrueBench) e envie-me seus resultados (saída da tela).
TOFFEE-DataCenter: Para as mesmas especificações semelhantes / similares, TOFFEE-DataCenter deve fornecer apenas metade do desempenho (velocidades WAN) em comparação com TOFFEE. O TOFFEE-DataCenter faz o processamento de pacotes do espaço de usuário e é muito mais versátil, flexível e modular. Devido a isso TOFFEE-DataCenter é capaz de otimizar os dados muito mais do que TOFFEE.
Escolhendo a RAM / memória para o seu dispositivo TOFFEE:
O dispositivo TOFFEE, assim como qualquer sistema Linux típico, precisa apenas de um mínimo
quantidade de RAM. Todo o processamento de dados de pacotes ocorrerá na sua RAM. De modo algum TOFFEE usa seu disco rígido (ou qualquer armazenamento secundário)
espaço para o processamento de pacotes. Então, se é Gigabit WAN ou dentro de velocidades de 100Mbps, escolha RAM que tenha cerca de 4-8GB de capacidade total.
No entanto, para alcançar o máximo desempenho ideal, especialmente para links WAN de alta velocidade, recomendo que você escolha RAM com velocidade máxima. Como DDR4 (com 2,8 GHz ou assim). Isso dá as melhores velocidades de interconexão do barramento de memória da CPU<>e melhora suas capacidades de processamento de pacotes do seu dispositivo TOFFEE. Isso também é, às vezes, aplicável, não apenas a criação de hardware TOFFEE, mas qualquer dispositivo de rede que lida com o tempo real processamento de dados / pacotes.
Escolhendo hardware do servidor para velocidades Gigabit (1G / 10G e assim por diante): Aqui estão alguns exemplos:
Lanner FW-8894 :: 1U High Performance x86 (Dual CPU) Network Appliance para Enterprise Firewall, UTM e IPS


Lanner NCA-5210 :: 1U Mid-range Modular x86 (Single CPU) Network Appliance for Next Generation Firewall, UTM e Segurança na Web


Lanner NCA-5510 :: 1U High Performance x86 (Single CPU) Network Appliance para Enterprise Firewall, UTM e IPS


* imagem cortesia Lanner Electronics Inc.
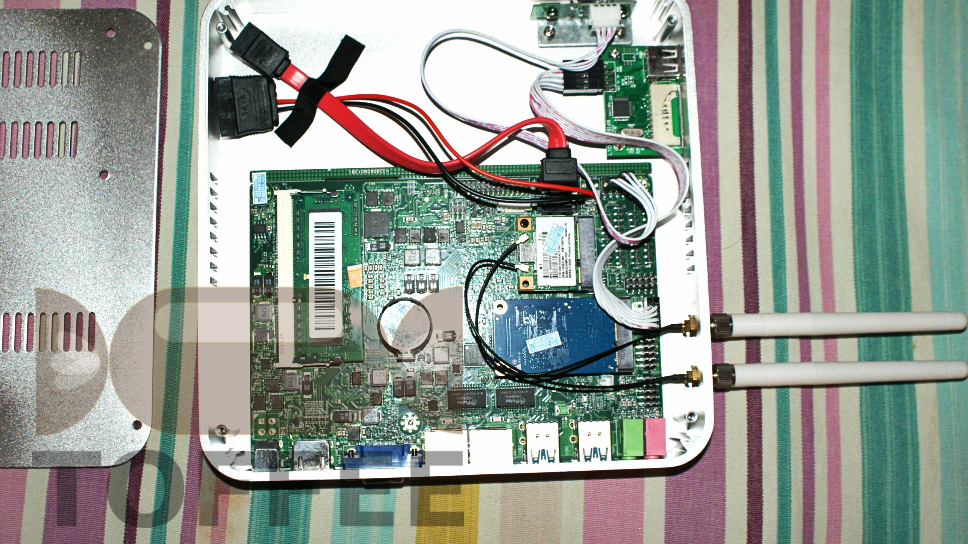
Uma amostra de hardware de baixo desempenho TOFFEE que eu construí:
Intel Celeron C1037U hardware sem ventilador
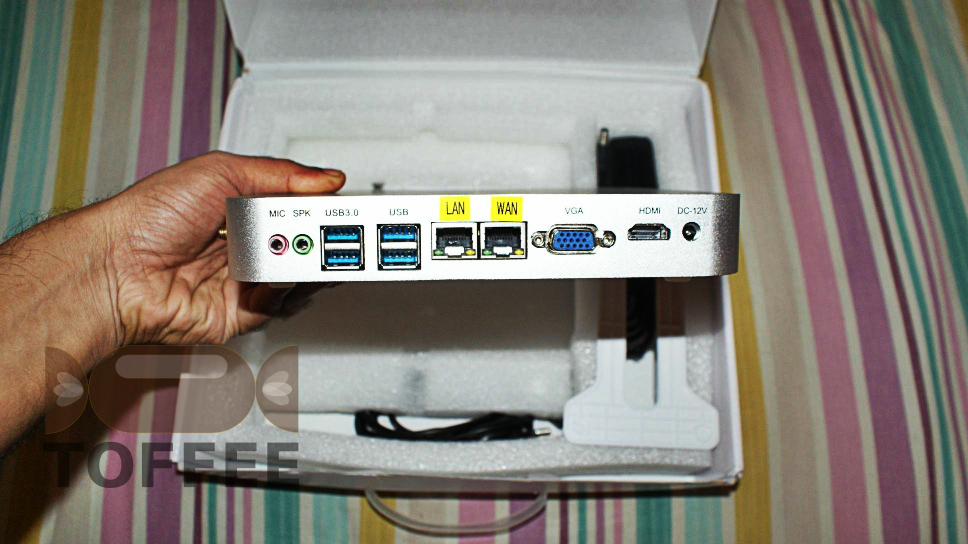


Referências:
- Raspberry Pi 2 Model B
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B
- ODROID-C2 - IoT single board computer(SBC)
- Lanner Electronics Inc.
Suggested Topics:
TOFFEE - WAN Optimization
| 💎 TOFFEE-MOCHA new bootable ISO: | Download |
| 💎 TOFFEE Data-Center Big picture and Overview: | Download PDF |

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
![]()
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021

Saturday' 13-Mar-2021
Featured Educational Video:
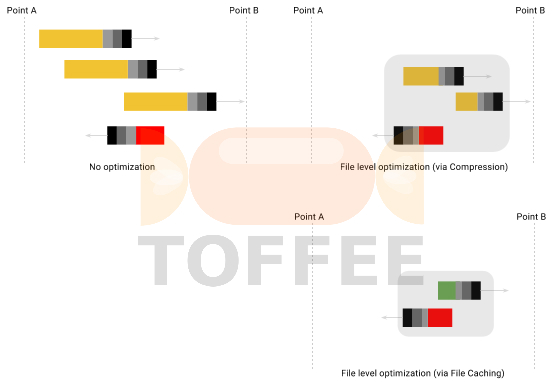
Research :: Optimization of network data (WAN Optimization) at various levels:
Learn Linux Systems Software and Kernel Programming:

Hardware Compression and Decompression Accelerator Cards:

TOFFEE-DataCenter on a Dell Server - Intel Xeon E5645 CPU:






